Bold new branding for end-to-end system integration specialists TGW Logistics represents confidence, flexibility and dynamism for a formidable presence in European and global logistics. Paul Hamblin hears about it.
The demands on logistics professionals may one day overwhelm. Take LogiMAT: now up to 10 halls (and counting), and with AI and robot technology making ever more outlandish promises to potential customers, how do you process what is actually real and what is not?
It is a landscape in which TGW Logistics – presenting new branding colours and shapes for an ever-changing world – promises an established, reassuring presence. “We are real. What you see is what you get,” says Jan-Willem Klinkenberg (pictured, below), Head of BizDev Northern Europe for the Austria-based global integrator.
End-to-end Integration
Let’s dig down into that reality a little. TGW describes itself as an end-to-end integrator, a term bandied around liberally in the marketing literature of many materials handling companies. What does it mean, though?
“It means we take full responsibility for the change your company is going through,” he defines. “Yes, that change is centred around warehouse automation, because that is our core business. But it’s important to bear in mind that we start by looking at the shed, the warehouse, as a total entity. The basic processes inside that shed comprise inbound, quality control, storage, picking, packing and shipping and this is where we will analyse the customer’s data to explore areas where we can deliver significant ROI via automation. Most of the time, but not always, this focuses on the picking and packing of small goods.”
Automation should not be simply dismissed as fewer people and more robots. Integration for experienced providers such as TGW Logistics is about partnering the customer to evaluate how to best deliver greater efficiency, speed, sustainability, flexibility and cost control. It can come in many forms.


Jan-Willem Klinkenberg, TGW
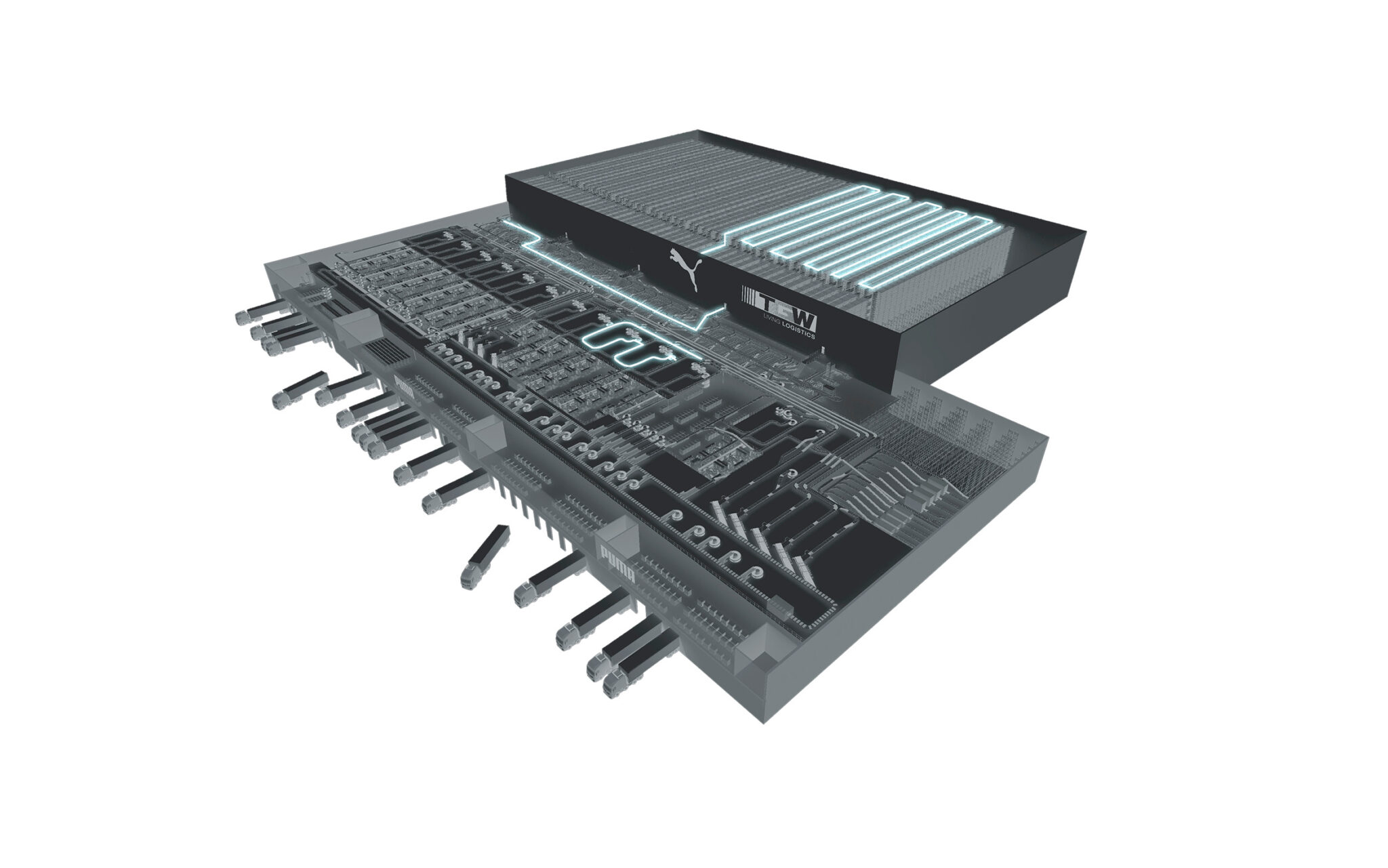
He illustrates: “One of the projects I’ve been involved with recently was a 50,000 sqm warehouse, in which we use just 8,500 sqm for automation. But 80% of the order lines go through the automation. The customer said to us, ‘Thank you, it’s fantastic, business case proven, budget and investment all signed off; now, can you help us with the other 41,500 square metres?’ They wanted us to deliver the WMS for the manual picking and packing areas, to support them in selecting the right pick and pack areas for what they called the heavy and ugly stuff, also for the pallet racking, the pick towers. That is real integration.
“Of course, the most added value for ourselves sits in the automation part, because that’s our core, it is our own kit that we have developed, produced and delivered. But ultimately we served this customer in a much wider journey to integrate five DCs into one new warehouse. It was a fantastic project, and I’d love to do more like it.”
An end-to-end integrator worthy of the definition needs agility to meet the demands of many types of customer, he explains.
“At the other end of the scale, for instance, we work with a major global ecommerce retailer, also a great customer and with fantastic projects. The added-value is a bit lower for us in their case because they have their own very accomplished in-house design teams. But they know exactly what they need from us, and so we are a significant system integrator for them, but without providing the full end-to-end processes and solutions.
“We are flexible to meet all needs – and we need both of those types of customers for our business.”
Automation is not new, of course. The technologies now refined and improved by TGW and others today have now been around for two, even three decades. Consequently, many new projects do not comprise the familiar ‘manual to automated’ transition, but a ‘legacy’ automated system to a state-of-the-art model. Decision-making is therefore on the agenda for many of those pioneers of the early 2000s.
“Take the UK, for instance. Some outstanding legacy systems were delivered to major retailers in the early years of this century. These businesses learned a long time ago the ROI potential and added value of automation. Now, 20 years later, they are in possession of outstanding technical equipment which is still there and which is still working perfectly. But they still have a decision to make in terms of remaining cutting-edge. What do they do? Do they buy new, do they reconfigure, do they dismantle?”
Easy decision, he reveals.
“Let me give you an analogy. Forty years ago, my mother and father bought a washing machine when they got married. And it’s still going strong. My father is so proud of it – ‘I replaced this, I replaced that, it’s still running!’ – and I said to him, ‘Dad, it uses five times as much water and 10 times as much energy than the latest models. Yes you’re doing OK, but if you get a new one you use less energy, less water and you’re going to make money.’”
Hardware and Software Expertise
TGW Logistics has evolved to suit customer needs as technology, habits and demands have changed. Founded 55 years ago in Austria, TGW was originally a small metalworking shop in the city of Wels; ‘software’ was barely a word in the dictionary. No longer. As software became an essential in the automation package, so TGW partnered with and then acquired specialist software companies, enabling it to accelerate and refine its in-house R&D investment.
“I always say that electro-mechanical equipment from TGW is the best in the world,” claims Klinkenberg. “That is not just sales patter; I can say it with proven confidence, because we have delivered to so many companies who are now massively successful in their own right, names such as Witron, Knapp, Vanderlande, SSI Schaefer.”

But the role of the right software, correctly applied and managed, is absolutely vital, he advises.
“Software comprises between 8-12% of the investment of an integrated system, but I believe 80-90% of the success of that system is down to the software. So it is of paramount importance. And a huge chunk of this importance is change management.
“The uninformed think that the integration and automation process is like buying a new car. Pick up the keys, jump in, drive away. That is categorically not the case here. It takes 6-12 months to make your assets sweat, to fully understand its dynamics and how it will work best for you. It’s the software that enables us to see what’s happening in real time, providing the customer with the evidence to improve future operations.”
Key Market Areas
TGW will apply itself to any relevant challenge in any sector, but is focused in four key areas: Grocery, Fashion/Apparel, Industrial and Consumer. The company has been a key part of the revolution in Grocery and Fashion over recent years.
He believes Grocery is advanced and well-defined. “It’s clear who all the players are. In the Nordics, Benelux, UK, you can count them on one hand or maybe two, all have invested in automation and all have already seen the added value of automation.
“In terms of coming trends, we’re noticing that some of our customers are trying to secure long-term partnerships with us for similar reasons. They all have the same issues: lack of labour – no one wants to work at night or in a deep freeze – so automation is the obvious answer. That means they need materials handling partners. In the Grocery sector, this translates to large-scale projects Those are good projects for us, we have the scope to take part in those tenders.”
In the Fashion sector, it’s no secret that a lot has happened over the past five years. “Covid was a massive factor. Ecommerce accelerated much faster, and now we’re seeing some evidence of the opposite happening as people show more willingness to go back to bricks and mortar stores for fashion items.” Omnichannel is therefore still very often the order of the day in fashion retail.
“As logistics experts we have to be able to deal with that, which means we need to be as flexible, scalable, and modular as we can with our solutions. Customers need to be able to handle single line orders, they need to be able to handle 25 or more lines.”
He explains that some of the new brands in fashion are very strong in marketing and sales but less so in logistics, thus presenting exciting opportunities for 3PLs. “You’ve seen 3PLs investing more in automation, in shuttle systems for instance,” he points out.
TGW’s latest tagline for its customers is ‘It’s Possible’. It’s a claim the company can make from a position of strength. Unlike some integrators, TGW develops and constructs all of its own equipment and hardware, backed by its own proprietary software. Crucially, the company is run as a Foundation, meaning that all decisions are taken for the good of the future health of the company, its people, customers and community, not to promote or protect a share price. That is a powerful starting place.
Finally, it’s projects are about partnerships. Customers learn from TGW experts; TGW is always learning from its customers. In that environment, everybody wins.
similar news
